The main classification of scrap wire and cable
According to voltage level:
1. Low-voltage cables: suitable for power transmission on AC 50Hz and rated voltage 3KV and below.
2. Medium and low voltage cables (generally refers to 35KV and below): PVC insulated cables, polyethylene insulated cables, cross-linked polyethylene insulated cables, etc.
3. High-voltage cables (generally 110KV and above): polyethylene cables and cross-linked polyethylene insulated cables, etc.
4. Ultra-high voltage cable: (275~800 KV).
5. UHV cables: (1000 KV and above).
According to the electric current:
1. AC cables (alternating current cables)
2. DC cables (direct current cables)
Classified by insulation material:
1. Oil-impregnated paper-insulated power cable. Its application history is the longest, and it is safe and reliable, with a long service life and low price.
2. Plastic insulated power cable, means the insulation layer is extruded plastic. Commonly used plastics are polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, and cross-linked polyethylene. The plastic cable has simple structure, convenient manufacturing and processing, light weight, convenient laying and installation, and is not restricted by the laying drop. Therefore, it is widely used as medium and low-voltage cables, and has a tendency to replace viscous-impregnated oil-paper cables.
3. Rubber insulated power cable. It is soft and flexible, and is suitable for occasions with frequent movement and small laying bending radius. The rubber materials commonly used for insulation include natural rubber-styrene butadiene rubber mixture, ethylene propylene rubber, butyl rubber and so on.

Recycling methods of waste cables
It is inevitable that some waste materials will be produced in life, but how to deal with the waste copper produced in various industries. According to the quality requirements of recycled products, the processing of waste copper can be divided into pyrometallurgical smelting and electrolytic smelting. The production of blister copper and copper alloys generally uses the fire method, while the production of electrolytic copper generally uses electrolysis.
Classification of scrap copper after recycling
A: Bare, uncoated and alloy-free pure copper wire, with no oxidation on the surface, no wool, and the diameter of the copper wire is not less than 1.6mm.
B: Clean, colorless, uncoated, tin-free, alloy-free pure copper wires and copper cables, and does not contain wool and burned fragile copper wires.
C: Unalloyed scrap copper wire contains miscellaneous materials, with a copper content of 96% (minimum content of 94%). It must not contain excessively leaded and tinned copper wires, soldered copper wires, brass and bronze wires, excessive oil, scrap iron and steel and non-metals, brittle burnt wires, insulated copper wires, and excessive fineness silk.
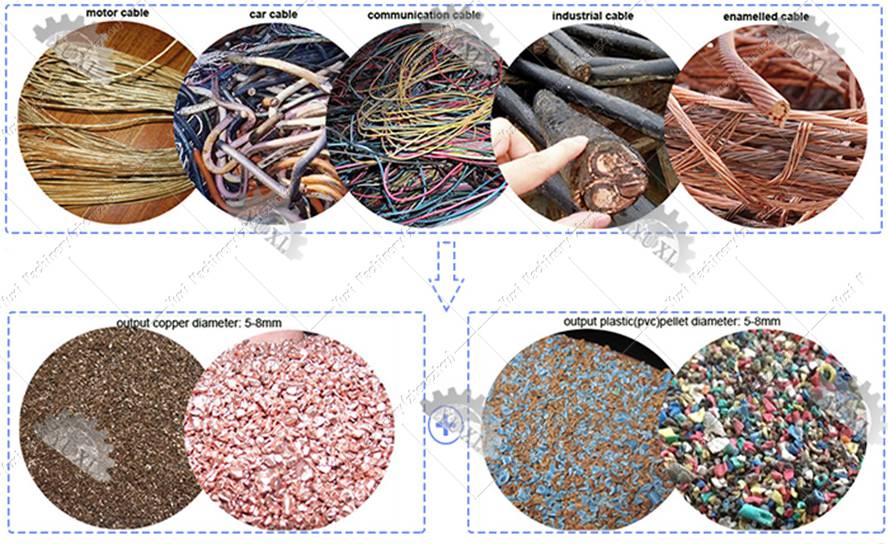
For recycling of scrap cable, we designed cable shredder machine which can be equipped with other optional equipment to be a cable wire recycling line.
Feel free to leave us a message for more details, thank you so much!
 Shredding Machine
Shredding Machine
 Waste Recycling Line
Waste Recycling Line
 Optional Equipment
Optional Equipment


